A fundamental piece of our sustainable future is already powering nearly every aspect of our lives. From the batteries in our electronics to the air conditioners cooling us off in the summer to solar panels providing renewable energy, copper is the lifeblood of our modern lives.
Copper is also essential to the innovations needed to combat the environmental challenges we face today, including climate change.
We know we will need more of just about everything that runs on copper as the world progresses toward reducing poverty. As millions are elevated into the middle class, the demand for air conditioning, refrigeration, consumer electronics, transportation and other staples of modern life will continue to increase.
Copper is already an essential ingredient in our most innovative technologies such as smart energy technology, aquaculture, space exploration and electric cars, so it is important to recognize that a low-carbon future requires more copper. Copper’s role in electromobility, energy efficiency and renewable energy is growing. McKinsey has estimated a 43 percent potential increase in copper demand by 2035 vs. today’s demand of 22 million tonnes.
The world will need to prepare to meet these increasing demands without jeopardizing the environment.


Source: Copper Applications Technology Roadmap (January 2017)
How can copper help to limit global warming and contribute to a brighter future?
Copper drives energy efficiency. Reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services is the most cost-efficient, large scale opportunity to reduce carbon emissions. Copper is the most efficient conductor of electricity and heating and cooling. Over their lifetimes, electrical systems containing one tonne of copper will emit between 100 and 7,500 fewer tonnes of CO2.
It can be re-used over and over again. Copper is 100 percent recyclable and never loses any of its properties. Every year, 8.5 million tonnes of copper are recycled. It can be recycled into diverse uses and objects after everyday products like cables and wires reach the end of their life. In fact, over a third of the copper used in the past decade came from recycled sources.
It puts the green in “green tech.” Emerging green technologies can help us combat climate change and reduce air pollution. Copper is essential in improving the performance of green technologies. It is already the key to renewable energy resources such as wind and solar, and future efforts are dependent upon copper.
There is a stable and plentiful supply. Copper is abundant with 720 million tonnes in known reserves according to USGS (2017). It is also key for the recycling of numerous other minerals like silver, gold and nickel. It is estimated that two-thirds of the 550 million tonnes of copper produced since 1900 is still in productive use (Glöser, 2013).

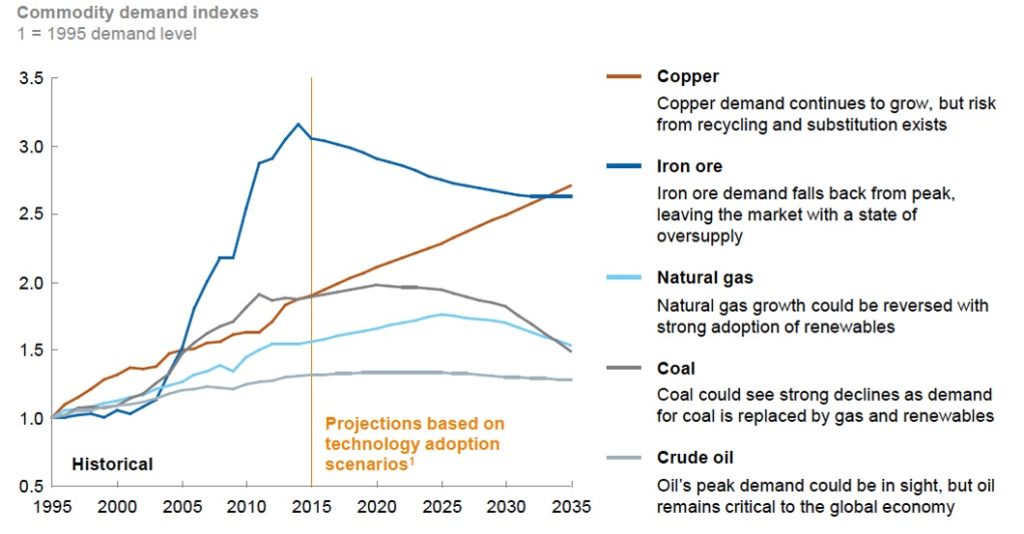
Source: McKinsey Global Institute. Beyond the Supercycle: How technology is reshaping resources. February 2017.
What is the copper industry doing to encourage innovation?
The copper industry is conscious of both its responsibilities for sustainable production and the enormous opportunities offered by a more prosperous and low-carbon future. We are also keenly aware that we need to “walk the walk.”
We are contributing to growth in communities. We recently completed a survey of 26 members representing 40 percent of world copper demand. These member organizations employ more than 300,000 people and are providing many local communities with schools, healthcare and water. Remote towns and communities that would otherwise vanish in the tsunami of urbanization depend on our members for their health and well-being. Our surveyed members invest $380 million in local communities each year.
We are driving sustainable production that protects the environment. We understand that the production activities driving growth in communities need to be water wise and energy efficient to minimize our impact on the environment and ensure a safe workplace. Future generations will not just judge us on what we produce but also on what we preserve.
In Europe, our members have reduced their energy consumption by 60 percent since 1990. Our members reported increasing their water recycling rate by nearly 70 percent over the past five years. Each year, our surveyed members invest more than $20 billion USD in improving the environmental and safety performance of their operations.
- Back in 2013, our member company Codelco installed a thermosolar plant at its Gabriela Mistral mine to generate an average of 54,000MWh/y and provide 85 percent of the power needed for its SX-EW copper plant. The installation has reduced the mine’s CO2 emissions by 15,000t/y. In 2017, Codelco promised to produce sustainable copper cathode over the next few years.
- Rio Tinto, another global member, reduced its GHG emissions intensity by 20.3 percent from 2008 to 2015, exceeding its set 10 percent target. By the end of 2016, the company had reduced its GHG emissions intensity by 26 percent.
We are an industry that endorses accountability. This includes publishing all relevant sustainability data and adhering to Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and similar initiatives.
We are investing in our low-carbon future. The industry continues to invest in new innovations to discover new ways copper can be used to reduce energy use. We work with governments across the globe to promote Best Available Technology and introduce standards for energy efficiency together with the UN as part of United for Efficiency (U4E).
As industry leaders, we must work together with policy makers to ensure we contribute to innovations meeting the increased demand for clean water, food, low-carbon electricity and clean air while combatting climate change and protecting the environment.
